
Are the Big Pharma corporations covering this up?
—-Important Message for Men in Pain—-
This “manly element” reduces arthritis and joint pain by 80%

You can get this natural powder at the supermarket dirt cheap…
It’s incredibly safe. Anyone can take it, even if you’re taking other things at the same time.
Some men report joint pain just “disappears.” Even people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis find relief with this.
———-
Mysterious element makes arthritis and joint pain disappear in men
You know how old-timers are always saying they can sense the rain in their bones before it happens?
Well I think I’m starting to develop that power.
But my doctor says it’s just arthritis.
Arthritis is a multifaceted disease with many causes, often characterized by inflammation and always by pain.
Specific types of arthritis range from the relatively innocuous, like crystal-induced arthritis, to the extremely dangerous and debilitating…
…like reactive arthritis, Lyme arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and the list goes on…
Yet science suggests that no matter what the specific origin of the joint pain, taurine will certainly help.
The reasons for this are many, but the majority of taurine’s benefits can be reduced down to 1 mechanism:
Taurine safely scavenges hypochlorite (OCl−) to form taurine chloramine:
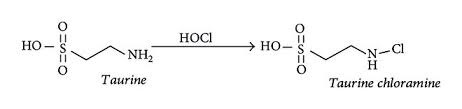
Hypochlorite (OCl−) is a damaging molecule formed by myeloperoxidase (MPO).
MPO is an enzyme released by neutrophils that is always found increased within inflamed joints (Edwards, 1988).
Taurine safely scavenges OCl− and the importance of this cannot be understated.
Hypochlorite has been shown to degrade hyaluronan (Schiller, 1996), a long chain polymer found in the synovial fluid that confers its lubricative properties.
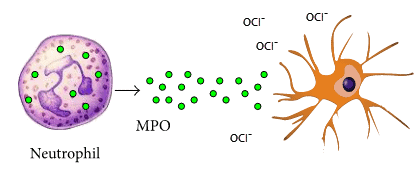
Besides being highly destructive, hypochlorite has also been shown to activate TRPA1 channels (Bessac, 2008) — a membrane receptor that mediates the sensation of pain in joints.
These two effects of taurine would be reason enough to consider taking it, but there’s more.
The product of the taurine hypochlorite reaction — taurine chloramine — has also been shown to be an important signalling molecule.
Taurine chloramine has been consistently found to downregulate many damaging cytokines and enzymes, including…
…cyclooxygenase‑2 (COX‑2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin‑1β (IL‑1β), tumor necrosis factor (TNFα), and neutrophil chemotactic factor (IL‑8).
Each one of these findings has been confirmed many times over by study groups in the United States, Poland, and South Korea. The sensing effect of taurine chloramine appears to be a “brake” mechanism for controlling cell damage.
That is to say, taurine chloramine seems to be used by the body as an indicator of too much hypochlorite being produced.
The cells then respond appropriately to limit further generation of hypochlorite by downregulating enzymes and cytokines involved in its production.
“Under these conditions TauCl therefore acts as a neutrophil-derived signaling molecule that is responsible for the down-regulation of production of inflammatory mediators by macrophages and neutrophils.” ―Marcinkiewicz, 1995
Taurine chloramine has also been shown to up-regulate antioxidant enzymes, such as heme oxygenase-1, glutathione peroxidase, NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase, and sulfiredoxin through the Nrf2 pathway (Kim, 2013).
So taurine not only prevents the formation of oxidants, it also lowers those already present.
Even though our body normally produces taurine, an extra gram or two per day should certainly help for arthritis.
Taurine naturally derived from methionine and cysteine, so supplemental taurine should have a sparing effect on these two amino acids.
Sulfate, a component of cartilage chondroitin sulfate, should also be spared, as it’s derived from cysteine.
So taurine is completely unique in the way it prevents damage, being both a hypochlorite scavenger and a signalling molecule.
Taurine also reduces pain and increases healing, 2 additional properties that make taurine an indispensable anti-inflammatory agent.
It is also completely safe and available online.
You could certainly expect taurine to work well on account of theoretical considerations, but there’s actually direct evidence of this.
This study below proves that it works, and also implies how much is needed:
This study took 50 rats and divided them into 5 equal groups, 4 of which were given arthritis by injection of Freund’s complete adjuvant.
This type of arthritis is called “adjuvant arthritis,” and occurs after T-cells become primed against one of the adjuvant’s components, mycobacterial Hsp60.
The T-cells then cross-react with a protein specific to the joints called aggrecan.
In this way, adjuvant arthritis is essentially reactive arthritis — a form of rheumatoid arthritis that occurs in people infected with certain bacteria, also shown to be caused by bacterial Hsp60.
So they’d found that of the 4 groups given adjuvant arthritis, swelling was reduced in 2: the high-taurine and diclofenac groups:
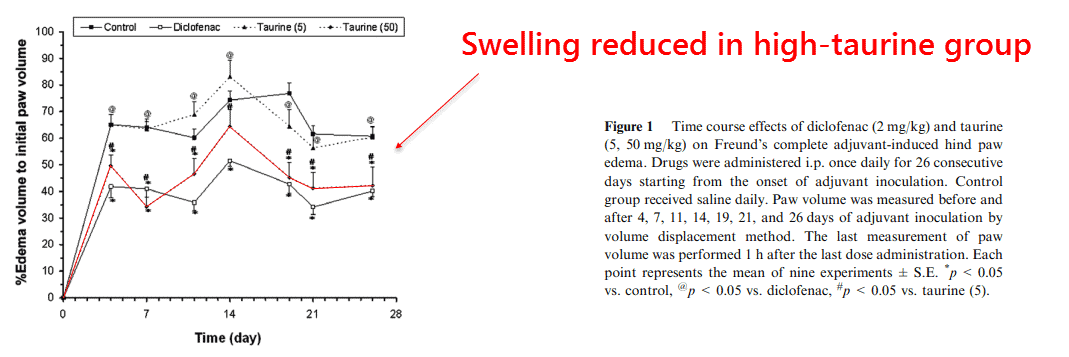
Diclofenac is a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, similar to aspirin, that works by reducing prostaglandin synthesis.
Although this is good for swelling, it probably does less in terms of controlling joint damage than taurine.
This is because taurine is also a hypochlorite scavenger, in addition to its ability to lower prostaglandins.
This beneficial effect was accomplished with 50 mg⁄kg taurine per day, a dose that corresponds to 3.5 grams for a 150 pound human.
This is similar to the 3g level shown to increase blood taurine levels by 33% in humans (Chauncey, 2003), an amount also synonymous with its Observed Safe Level (Shao, 2007).
Taurine is so safe that they couldn’t set a standard NOAEL upper limit.
The researchers had also found that TNFα and IL‑1β, the two main “inflammatory” cytokines, were also decreased by taurine:
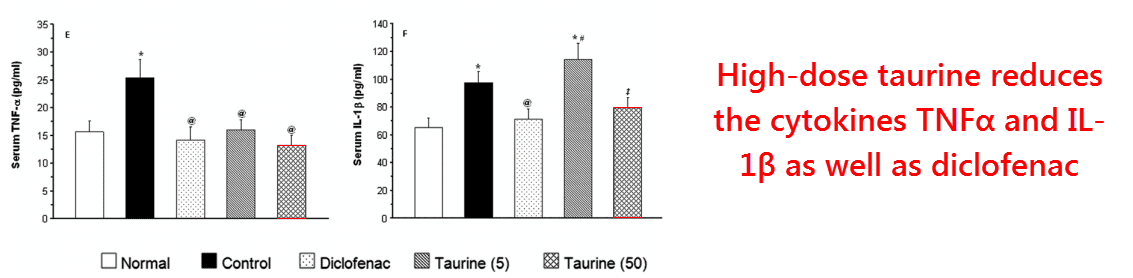
This finding is nothing new, however.
It has already been demonstrated before in vitro in mouse macrophages (Marcinkiewicz, 1995), mouse polymorphonuclear leukocytes (Kim, 1996), and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (Park, 1998).
The inhibition of TNFα is especially important as this upregulates TRPA1 ion channels in the joints, a receptor shown to cause the long lasting pain characteristic of arthritis (Fernandes, 2011).
The anti-cytokine effect is always mediated by taurine chloramine, not taurine itself.
This means that taurine is not a global immunosuppressant per se, but merely puts a brake on “inflammation” in certain areas high in hypochlorite.
The more taurine within the synovial fluid, the lower the threshold at which the inflammatory/anti-inflammatory transition occurs.
More taurine should thus translate into less joint damage, pain, and swelling.
And all of these symptoms are downgraded by more than one mechanism.
The fact that taurine is a scavenger of hypochlorite makes it hard to imagine a better supplement to take.
Especially considering that neutrophils, myeloperoxidase (Edwards, 1988), and chlorinated peptides — a biomarker for hypochlorite — are all elevated in rheumatic joints (Steinbeck, 2007).
“We have shown that the presence of Cl-peptides in synovial fluid is unique to subjects with active cartilage degradation.” ―Steinbeck, 2007
Hypochlorite has also been shown to cleave hyaluronan into smaller fragments in vitro (Baker, 1989).
Smaller fragments of hyaluronan are exactly what’s found when analyzing the joint fluid from rheumatic cases (Dahl, 1985).
Besides acting as the primary lubricant in joints, hyaluronan is also responsible for resisting compression.
But that’s not the only evidence for how hypochlorite causes the condition.
Because 4 popular arthritis treatments — ᴅ‑penicillamine, tiopronin, sodium aurothiomalate, and aurothioglucose — have all been shown to scavenge hypochlorite (Cuperus, 1985).
Taurine also scavenges hypochlorite, but has the additional properties of being natural, affordable, safer, and able to transform into an anti-inflammatory signalling molecule in the process.
“Therefore, the main role of Tau‑Cl seems to be the protection against HOCl‑mediated tissue destruction.” ―Kontny, 2002
It is the numerous and redundant anti-inflammatory effects of taurine that make it perhaps the best all-around arthritis supplement.
That is to say, taurine does nearly everything you’d want and does so in multiple ways:
- It scavenges hypochlorite directly (Lee, 1992)
- It lowers it more by downregulating the neutrophil chemoattractant IL‑8 (Kanayama, 2002)
- And lowers it even more so by reducing myeloperoxidase synthesis through HO‑1(Kim, 2010).
It also inhibits pain in multiple ways:
- By scavenging hypochlorite, an activator of TRPA1 channels (Bessac, 2008).
- By reducing TNFα, a cytokine that upregulates TRPA1 channels on synovial cells (Meng, 2016).
- By reducing COX‑2, an enzyme that produces prostaglandin E2 — another pain-inducing molecule (Kontny, 2003).
Last but not least, it spares the amino acid cysteine, and by extension sulfite.
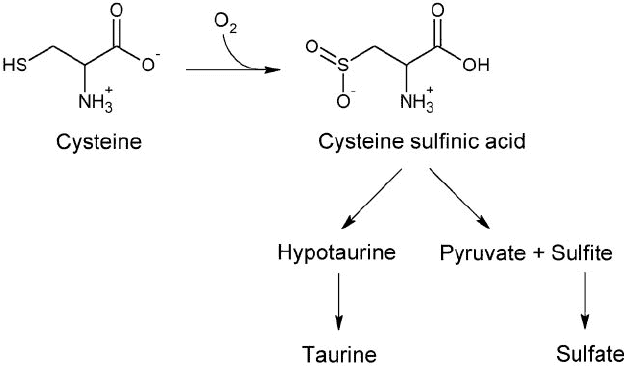
Sulfate is useful for many things, not the least of which are the joints.
Cartilage has a very high concentration of chondroitin-6-sulfate, a long chain polymer that requires sulfate for its synthesis.
Such are the many benefits of taurine, the only OCl scavenger that becomes an anti-inflammatory signalling molecule in the process.
“These combined results suggest that the inhibition of ṄO and O2− production by Tau‑Cl protects cells from inflammatory injury caused by overproduction of reactive nitrogen/oxygen species.” ―Kim, 2006
Taurine also protects against gastric cancer by the same OCl− scavenging mechanism (Murakimi, 1989), so there’s no reason not to take it.
—-Important Message From Our Sponsor—-
Back by popular demand: the Midnight Pearl Stiletto — get it for less than $6
- Spring Assisted Knife
- 8.5″ Overall Length – Very Sharp
- 3.5″ Black Ceramic Coated Stainless Steel Blade – Stiletto Design
- 5″ White Pearl Handle – Very Comfortable Grip
- Includes Belt Clip
- Liner Locking System
It’s up on our website for $40…but I worked out a deal for the next 100 guys who can’t wait to get their hands on this sick EDC…
So you’ll pay less than $6 if you act within the next few hours.
These are guaranteed to sell out, so grab yours here and be prepared wherever you go.
———-
