
[cmamad id=”26353″ align=”center” tabid=”display-desktop” mobid=”display-desktop” stg=””]
Why are doctors telling people to take leucine?
—-Important Message From Our Sponsor—-
FREE training – ditch your 9 to 5 and make $100,000 a year

Picture this… You’re at work, slaving away as usual…
You know your boss is in a foul mood, and normally you’d keep a low profile.
But not today.
So when you see him stalking in your direction, you just smile.
He screams at you, dropping f-bombs and other expletives as his warm breath washes over you.
Your reaction?
You simply stop your work, give him the solitary middle digit, and walk out.
And you never go back…
That might seem ridiculous right now, but that will soon change.
Because these methods will let you go from barely paying the rent in a crappy apartment to an international jet-set lifestyle in just a couple of years.
And you can create an “escape hatch” from the soul-sucking 9-to-5 everyone else is trapped in.
———-
Leucine: Cause of Cancer or Cancer Cure?
Of the nine essential amino acids, two of them stand out as powerful cancer-promoting agents: methionine and leucine.
This is because they work on every individual cell to promote growth…
They don’t need to act on a particular amino acid (for example) such as tryptophan, which, after becoming serotonin, releases growth hormone from the pituitary.
(I’m not a fan of tryptophan either…but that is another newsletter…)
Let’s start with methionine, which is very common in foods such as meat and fish.
Mice given a low-methionine diet lived 40% longer than any other mice.
And…
Methionine strongly promotes cell replication by becoming polyamines everywhere…
And these interact with DNA directly. Not in a good way either.
Polyamines from methionine actually provide the force that unfurls the double helix of DNA.
Leucine is the only other amino acid that can approach the powerful growth effects of methionine…
It does this through a special receptor that senses only this one amino acid.
So, like methionine working physically on DNA, after becoming polyamines, leucine also increases proliferation.
But it does it in a different way.
Leucine works though transmitting a powerful growth signal – it does this almost “hormonally.”
Bodybuilders know about this…
They often supplement either leucine or branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) for increased growth.
But these same anabolic effects peculiar to just this one amino acid (leucine) also make it a powerful tumor growth factor…
In fact, more so than any other BCAA.
But oddly, leucine is actually sometimes actually prescribed for cancer patients in the hope of reducing muscle wasting (cachexia).
“However, the rates of protein synthesis increase to a much greater extent in tumors than in muscle, suggesting that, while leucine supplementation may protect against cancer-associated cachexia, it may also enhance the progression of the cancer.”
So… Since leucine undoubtedly promotes cancer growth, this is a terrible idea.
It is much better to be skinny than to have cancer.
This effect had actually been known since the early 1980s:

This study took place in 1986, just a few years after screenings revealed that leucine has peculiar cellular effects.
It was a simple study.
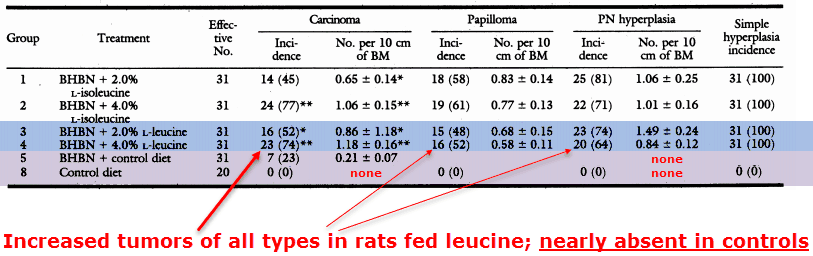
They gave rats a standard carcinogen that induces tumors.
And they also gave groups of the rats either leucine, isoleucine, or no supplement.
And they found that only a 2% leucine addition to their food dramatically increased tumor size and number.
The control rats were able to recover, remaining for the most part cancer-free:
These early studies had discovered the well-known mTOR pathway before it was formally acknowledged.
(The mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway integrates extracellular and intracellular signals. It serves as a central regulator of cell metabolism, proliferation, growth, and survival.)
This pathway ends with increased fatty acid synthesis, insulin resistance, protein synthesis, and very often cell division.
Most amino acids don’t do this, and athletes know it.
“These results confirm that L-isoleucine and L-leucine have tumor-promoting effects on bladder carcinogenesis in rats.”
This line of research had to wait 25 years to be confirmed…
It was first resurrected by MIT in 2011, then by the Japanese in 2012, by Doctor Kristyn A Liu (U of Texas) two years later, and then finally in a Chinese article published just last year.
The first modern study was informative…
But it used a genetically-bred cell strain with a modified mTOR pathway – the very site of leucine’s action – thereby confounding results.
Nonetheless, it showed that you can create a cancer strain by interfering with leucine signaling.
And one of the modern studies (Xie, 2012) was essentially a repeat of the 1986 study of mice and bladder cancer…showing the exact same thing.
Although redundant, it does add verification.
‘The incidence of larger tumors at week 29 in the AIN-93G diet group supplemented with L-leucine was significantly increased compared to the control;’ ―Xiao-Li Xie
But the one published in 2014 by Liu has more relevant findings:

They used four groups of rats with pancreatic cancer.
They gave two of the +5% leucine subgroups separate caloric intakes – one group got only 70% of the caloric intake the other group received.
Not surprisingly, this small change of amino acid ratio caused a large change in tumor size:
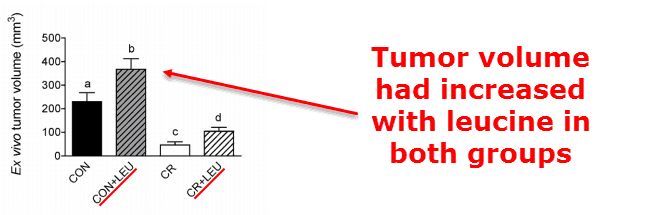
This also occurred in the rat groups consuming less food in general, the ones given 70% of the standard calories.
All four groups showed dose-dependent tumor growth with leucine.
This study also showed that the mTOR pathway is involved.
The mTOR sensor was activated by leucine (through phosphorylation), going on to regulate the cell cycle through cyclin D1 (a protein that is misregulated in many cancers):
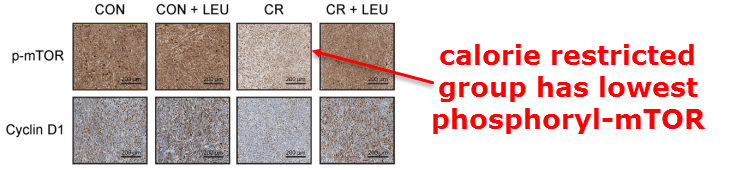
This is important, because mTOR also controls autophagy (intracellular protein recycling).
So not only does leucine promote cancer growth, but restricting it can help dissolve existent tumors.
This effect on autophagy (the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells) was observed as early as 1981…
The addition of just this one amino acid out of seven tested reduced autolysosome count. (Autolysosomes are involved in autophagy.)
“Our results indicate that leucine plays a unique role as a regulator of bulk autophagy…”
And the seven amino acids tested were the strongest ones, as previously discovered.
So leucine inhibits autophagy more than any other amino acid…
[cmamad id=”26354″ align=”center” tabid=”display-desktop” mobid=”display-desktop” stg=””]
And that means that it inhibits the self-absorption of tumors more than any other amino acid.
And it’s doing that at the same time that it’s increasing proliferation.
Leucine acts through mTOR like a switch…
It controls two separate synergistic processes simultaneously.
This explains why such a small change can have such a dramatic effect.
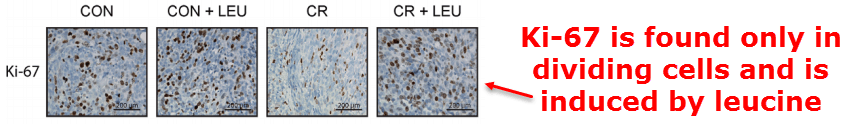
To repeat, Leucine increases protein synthesis while, at the very same time, limiting its destruction…
This amplifies growth in two different ways through sensing small dietary changes in the leucine ratio.
“Findings in this report demonstrate for the first time that dietary leucine supplementation increases growth of pancreatic tumors.”
And the newest study, done last year, showed the same.
They injected cancer into mice and fed half the groups a leucine-restricted diet.
The mice lived for the length of the study (four days), and the results are shocking:
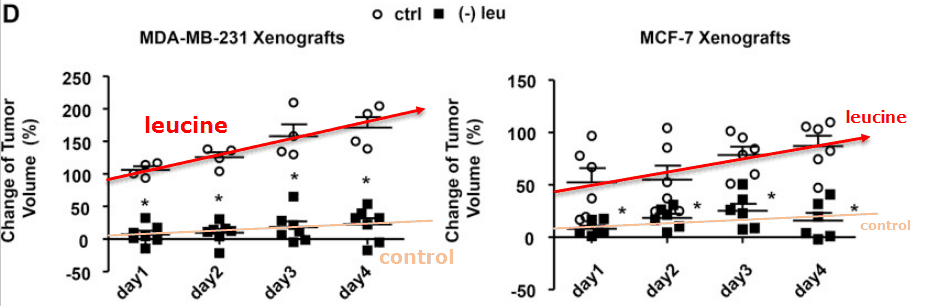
These were adult mice, so they already had quite a bit of stored leucine inside their bodies.
The blood levels of this amino acid dropped by roughly half during total leucine restriction, perhaps explaining the very small amount of growth seen in the control group.
Part of the mechanism through which leucine increases growth is by upregulating an enzyme called fatty acid synthase.
This enzyme is needed to create new fatty acids for the cell membrane, which needs to grow before the cell can divide in two.
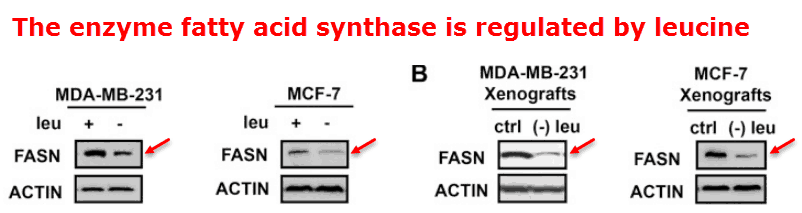
So, like methionine, leucine is unique to the extent that it can strongly promote cell growth.
This fact can be useful for some – such as certain athletes – but a detriment to others.
And it actively inhibits autophagy as well – so too much of it will inhibit protein turnover.
Consuming foods with a low leucine and methionine ratio would tend towards reduced growth (i.e. apples, tomatoes, berries, cucumbers, cabbage).
Adding gelatin, which has eight amino acids and no leucine, would reduce the ratio further.
‘By using pair-fed mice as a control, we demonstrate that the reduced tumor growth was caused primarily by deficiency of leucine, rather than the reduction in food intake.’ ―Xiao
—-Important Message—-
This shower activity gives men strong, long-lasting erections – works better than pills

I’ve discovered something men can do at home by themselves in the shower (or with a partner) that makes erections stronger and longer-lasting…
Even if it’s been years…
Even if you’ve given up…
And even if you just want a little extra “oomph” down there to surprise her with…
———-

- X Nishio, Yasunori. "L-isoleucine and L-leucine: tumor promoters of bladder cancer in rats." Science (1986)
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/231/4740/843.short - X Sheen, Joon-Ho. "Defective regulation of autophagy upon leucine deprivation reveals a targetable liability of human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo." Cancer cell (2011)
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f795/4a5df4b3692359d24cfb490f271cec5751ce.pdf - X Xiao, Fei. "Leucine deprivation inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human breast cancer cells via fatty acid synthase." Oncotarget (2016)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5325395/ - Grinde, Bjørn. "Leucine inhibition of autophagic vacuole formation in isolated rat hepatocytes." Experimental cell research (1981)
www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0014482781904602 - X Liu, Kristyn A. "Leucine supplementation differentially enhances pancreatic cancer growth in lean and overweight mice." Cancer & metabolism (2014)
https://cancerandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/2049-3002-2-6?site=http://cancerandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com - X Xie, Xiao-Li. "Long-term treatment with L-isoleucine or L-leucine in AIN-93G diet has promoting effects on rat bladder carcinogenesis." Food and chemical toxicology (2012)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278691512005418
