
The shrinking effect leads scientists to discover this impotence fix that any man can use tonight
—-Important Message—-
Peruvian jungle juice makes men bigger and fatter “down there” naturally

A successful trip to Peru and a chance meeting with a gorgeous indigenous woman landed me this secret recipe…
…a jungle juice recipe that’s been used for over 100 years…
And believe it or not, this juice makes it easier for men to get rocky, stay rocky, and perform at their best with a woman.
It’s a natural miracle brew that’s allowed me to sport the strongest, most impressive looking erections whenever I want.
Want to try it? Click here and taste it for free.
———-
Scientists: why penis shrinks in cold reveals impotence cure
Incredible story today about how the cold shrinking penis reveals a cure to impotence.
Let’s start with sildenafil — the brand name rhymes with “niagara” — when it hit the market, the most popular treatments for inducing penile firmness were alpha blockers – usually through direct penis injection.
This is for good reason.
Alpha-adrenergic receptors are found in the corpus cavernosum (tissue that forms the bulk of the penis).
They outnumber beta-adrenergic receptors by 10 to 1 (Levin, 1980), and muscarinic receptors by 15 to 1 (Costa, 1993).
Here they actively contract the trabecular meshwork of the penile shaft, inhibiting blood engorgement and firmness.
Adrenergic receptors are also found in the pudendal artery which supplies the member with blood, which they also tend to contract.
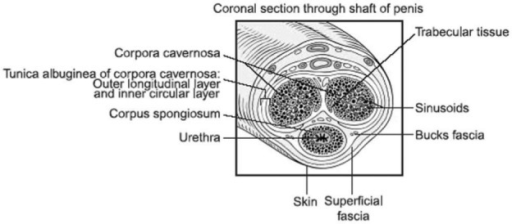
So alpha‑adrenergic receptors are quite prevalent and important in the penile shaft…
And in all cases they act to inhibit erections by contracting muscles and thereby reducing blood flow.
This is likely why cold temperature, which releases adrenaline, is commonly known to cause a shrinking of the member.
Stress is another factor that releases adrenaline and noradrenaline, perhaps explaining why nervousness also tends towards inhibition.
High blood levels of noradrenaline have even been found to be associated with impotence as compared to controls, and also with the ability to respond to treatment (Chul Kim, 1992).
“The level of norepinephrine was higher in patients with psychogenic impotence than in normal controls and patients with vasculogenic impotence, and it was significantly higher in negative responders than in positive responders in the psychogenic impotence group.” (Sae Chul Kim, 1992)
The inhibition that alpha -adrenergic receptors have over the erections response is so profound that phenylephrine, an alpha-adrenergic agonist, is the first-line treatment for priapism (Wen, 2006) – a condition of sustained boner that lasts over four hours.
Injection of noradrenaline has even been used to interrupt erections during urethral surgery (Meyer, 1986).
Conversely: an overdose of prazosin, an alpha-1-adrenergic blocker, has been shown to actually cause priapism (Robbins, 1983).
It should then be no surprise that nearly all pre‑sildenafil treatments used to enhance erections were alpha-adrenergic blockers.
For example apomorphine, yohimbine, or papaverine, a potent phosphodiesterase-10 inhibitor (IC50 = .36 μM).
These treatments were all highly effective and still are…
The main reason they fell into disuse was because they are natural and thus cannot be patented.
Although papaverine and apomorphine are both natural treatments, papaverine is derived from the opium poppy and apomorphine can easily be converted into morphine.
Partially for these reasons, both papaverine and apomorphine are currently prescription-only treatments in the US.
This leaves us with yohimbine, a potent and selective alpha-2 blocker – and also melatonin and DHEA.
Just one milligram of melatonin has been shown to reduce norepinephrine levels by 30% (Arangino, 1998).
And maybe that is the reason why it has been shown to restore erections in impotent rats (Drago, 2000).
In accordance with this, impotent men have been shown to have 24% lower basal melatonin levels than controls (Bozkurt, 2018).
Melatonin has been shown to decline considerably with age (Sharma, 1989)…
So, besides the concomitant reduction of DHEA (a proto-androgen), this is another hormone that can explain the increasing rates of impotence every year after 20 to 30.
Melatonin, DHEA, and yohimbine are three safe supplements that you can buy online and have at your house in under a week, and all for under $50…
So we’ll focus on these.
Topical papaverine gel is also quite effective (Kim, 1995), but you’d have to get a prescription for that one.
“After application of a 15% and 20% papaverine base gel to the scrotum, perineum, and penis, cavernous artery diameter was significantly increased (36%) as assessed by color flow Doppler ultrasound.” (Edward Kim, 1995)
Besides alpha-blockers and phosphodiesterase inhibitors, other treatments shown effective are:
- Calcium channel blockers
- Dopamine agonists
- Prostaglandin E1
All other treatment types have no effect when introduced intracavernously.
Combinations of these can be extremely effective.
For instance, administration of Ceritine (a treatment composed of an alpha-1 blocker, an alpha-2 blocker, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and a dopaminergic agonist) has been shown to restore erections in 91% of impotent men (Virag, 1991).
Yohimbine is a classic alpha-2 blocker, so it should be no surprise that it’s also quite effective.
Yohimbine had been well known to antagonize adrenergic receptors since the 1940s (Loew, 1948), and considered an aphrodisiac even longer (Brandenberg, 1927).
Due to its potency and selectivity for the alpha-2 subtype, it’s been routinely employed in pharmacological studies ever since.
| Here is some science stuff: Yohimbine has a Ki of 1.05 nanomolar on α2A‑receptors and 1,680 nanomolar on α1A‑receptors. |
This potency and this selectivity are the reasons why yohimbine is the preferred pharmacological agent for studying alpha-2 receptors among all treatments currently known, either natural or synthetic.
Yohimbine is quite effective, just as you’d expect of a potent alpha-2 blocker.
Although there’s no data on its use topically, there’s plenty of studies examining its effects orally:

These authors analyzed all yohimbine studies they could find on penile function, eventually settling on seven studies that matched their inclusion criteria.
They used the best and most reliable data; only randomized, placebo controlled, double‑blind clinical trials were even considered for inclusion.
What they found was a consistent and significant effect over placebo, with a combined odds ratio of 3.85.
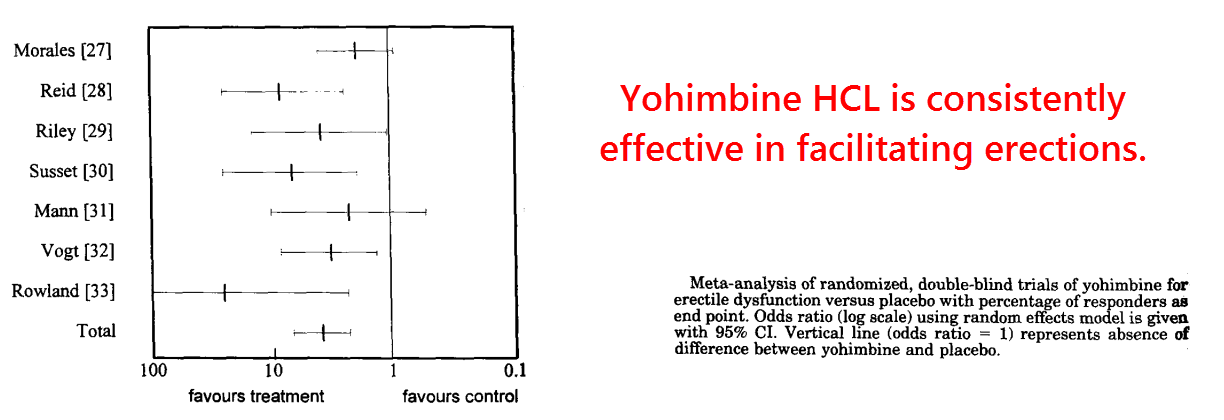
In all instances in the graph above, except for the Sussett study, the doses were between 5-10 milligrams taken three times a day.
A more inclusive meta-analysis conducted two years previously had also shown favorable results (Carey, 1996).
This study analyzed the same studies as Dr. Ernst above, but also examined uncontrolled trials and studies where yohimbine had been used in combination with other things.
There are also many rodent studies to go on. But, as always, human studies are preferred when available.
The studies of yohimbine conducted after this meta‑review are also favorable.
But since this study was published the same year that sildenafil hit the market further studies were few in number.
“We have presented objective evidence that yohimbine has a positive effect in men with organic erectile dysfunction.” (Guay, 2002)
Yohimbine appears to work primarily through the blood vessels supplying the penis, and perhaps also via the veins leading out.
This is because alpha-1 receptors are more prevalent in the corpus cavernosum, and alpha-2 receptors are more prevalent in the arteries and veins.
In the corpus cavernosum, the alpha-1 blocker prazosin was 300 times more effective than rauwolscine (a stereoisomer of yohimbine) in inhibiting contractions induced by norepinephrine.
In the cavernosal artery, however, both prazosin and rauwolscine had about the same effect (Hedlund, 1985).
This means that alpha-1 receptors equal alpha-2 receptors in this location.
This is partially why Ceritine (a treatment containing both alpha-1 and alpha-2 blockers) is so effective, working in 91% of those who take it.
So, although yohimbine is not quite the magic bullet that Ceritine is, it is still a necessary component of it.
You could argue that Ceritine wouldn’t be as effective without its alpha-2 blocker.
“Collectively, these results leave little doubt that yohimbine is superior to placebo in treating erectile dysfunction.” (Ernst, 1998)
Simply lowering plasma epinephrine + norepinephrine would be tantamount to taking an alpha-1 and an alpha-2 blocker together.
And for this reason melatonin should not be discounted.
Melatonin is by far the most potent hormone in the body… so a little bit goes a long way.
For instance, even a low 500 MICRO-gram (NOT milligram; this is ONE HALF of a milligram) dose has been shown to quadruple the plasma levels of the normal melatonin peak.
So even a lower dose may be preferred (Gooneratne, 2011).
Since melatonin is sold in doses as high as 20 milligrams, there’s plenty of room for abuse here. That’s at least 40 times MORE melatonin than is desirable.
And I think 100 MICRO grams of melatonin may be safer.
The lowest dose sold commercially is 300 micrograms, and one third of one of these is all that a person should need.
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is also quite useful, but effects do take time as it must convert to testosterone first.
Androgens act to upregulate nNOS (Nitric oxide synthase) in the penis (Park, 1999), and also the tyrosine hydroxylase needed to produce dopamine (Keast, 1999).
It could be worth noting that besides being an alpha-1 blocker, apomorphine is also a dopamine agonist.
This could be why it’s been shown so effective, being used about as much as papaverine in the pre‑sildenafil era.
The most effective treatments that increase erections are listed below:
- Alpha-1 blockers such as phentolamine and prazosin
- Alpha-2 blockers such as yohimbine and rauwolscine
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors such as papaverine
- Dopaminergic agonists such as apomorphine
- TRPA1 activators such as prostaglandin E1
- Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil
—-Important Message—-
This simple shower method reverses all 3 kinds of “rockiness” problems
There’s something I’ve been doing in the shower that gives me stronger, longer-lasting “rockiness” when I’m with my wife…

It’s super simple, and it actually feels really good…
And it does more for my power and stamina than any pill or supplement.
I shared it with a friend of mine and here’s what he said:

And don’t worry because if you’re single, you can still do this shower trick and it will improve your performance for the next time you’re with a woman.
Try this next time you’re in the shower for stronger, longer-lasting “rockiness.”
———-
